What Constitutes an Agenda in Business Meetings?
A well-crafted agenda is a critical component in the orchestration of effective business meetings. Serving as a roadmap, an agenda outlines the specific topics and activities planned for discussion, ensuring that the meeting achieves its intended objectives efficiently. This article delves into the elements that constitute a robust agenda and the impact these elements can have on the productivity of business meetings.
Purpose Statement
Every agenda should begin with a clear purpose statement. This statement sets the tone for the meeting and informs participants of the meeting’s goals. For example, the purpose might be to strategize for an upcoming project, resolve outstanding issues, or make critical decisions. A clear purpose ensures that participants understand the importance of the meeting and come prepared, significantly increasing the meeting's effectiveness.
List of Topics
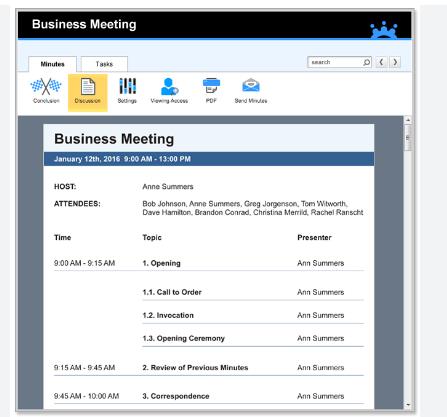
The core of any agenda is the list of topics to be discussed. Each topic should be clearly defined and prioritized according to its importance and relevance to the meeting's goals. For instance, critical issues requiring decisions should be placed earlier in the meeting when participants are most alert. According to management studies, meetings where topics are prioritized and time-bound are 30% more productive than those that lack structured agendas.
Time Allocations
Assigning specific time slots to each topic on the agenda helps in managing meeting time efficiently. Time allocations prevent any single discussion from dominating the meeting, ensuring that all relevant issues receive attention. This practice not only keeps the meeting on schedule but also respects participants' time, a fundamental aspect of maintaining high engagement levels.
Participant Responsibilities
For each topic, it’s beneficial to assign a lead or responsible person who will guide the discussion or presentation. Identifying these roles in the agenda informs individuals of their responsibilities ahead of time, allowing them to prepare adequately. This preparation reduces downtime during the meeting and enhances the quality of the information shared.
Preparation Requirements
The agenda should clearly outline what participants need to prepare before the meeting. This might include data reports, documentation, proposals, or pre-reading materials. Providing this information upfront ensures that all participants come prepared to contribute effectively, enhancing the productivity of the discussions.
Questions for Consideration
Including specific questions or points for consideration under each topic can guide discussions and stimulate critical thinking among participants. This method encourages active participation and ensures that discussions remain focused on outcomes rather than devolving into aimless conversation.
Conclusion and Next Steps
At the end of the agenda, it’s prudent to include a segment dedicated to wrapping up the discussed topics and outlining next steps. This section should detail the actions to be taken post-meeting, the individuals responsible, and any deadlines for these actions. This clarity in follow-up tasks ensures that the meeting results in tangible outcomes and accountability.
For those looking to optimize their meeting planning process, further insights and tips can be found at What is a Agenda.
Conclusion
An effective business meeting agenda is a meticulously structured document that ensures meetings are purposeful, time-efficient, and productive. By incorporating the elements outlined above, organizations can enhance their meeting outcomes, fostering a culture of efficiency and accountability. With the right agenda, meetings can transform from often-dreaded events into powerful tools for collaboration and decision-making.
